Glycotoxins in Browned, Overcooked Foods May Cause Alzheimers
Recent studies with mice has provided another clue in the puzzle to reveal the cause of Alzheimers Disease and dementia.
Cooking vegetables is known to release more vitamin in foods by breaking down cell walls and changing some nutrients into a form that can be readily absorbed. Cooking also makes food more palatable.
However, overcooking and 'browning foods' denatures protein, destroys vitamins and removes many nutrients in the food.
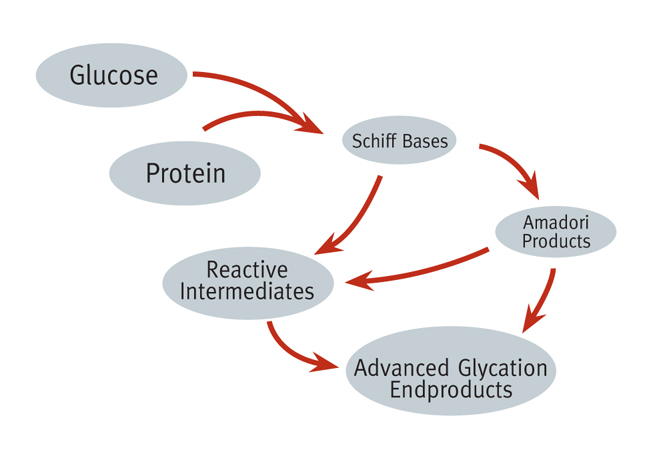
The browning of foods occurs through a process known as glycation, when a sugar molecule, such as fructose or glucose are bound to protein molecules.
This produces what are called glycotoxins. This process can occur within the body or externally when food is cooked or prepared prior to being eaten. Glycotoxins are also referred to as Advanced Glycation Endproducts (AGEs).
These changes did not occur in mice fed on a low-AGEs diet.
When the AGE levels of a group of about 100 healthy humans were examined there was a correlation between AGE level and amount of cognitive decline and insulin resistance in the subjects.
This article reviews the evidence that glycotoxins could be a potential cause of dementia, Alzeimers Disease and diabetes.
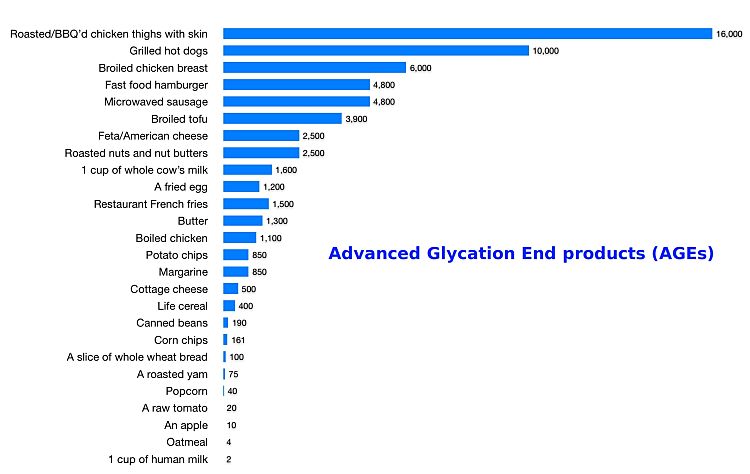
Glycotoxins - Food Sources and Origins from Cooking
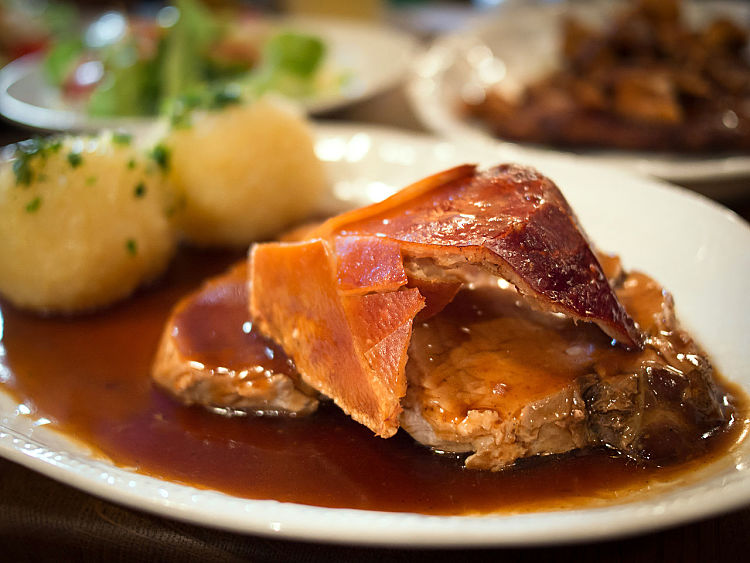
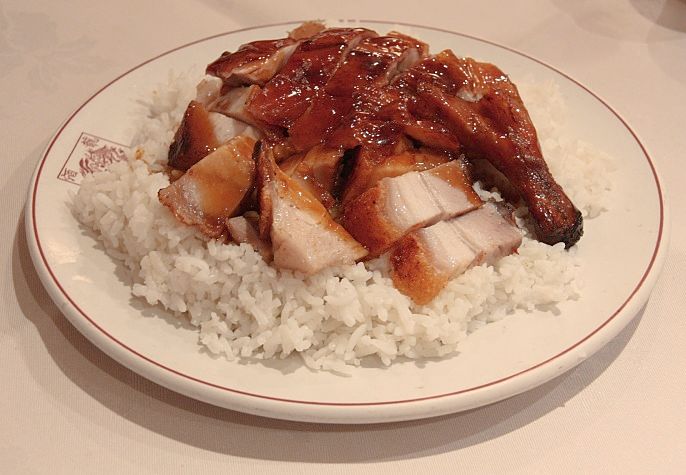
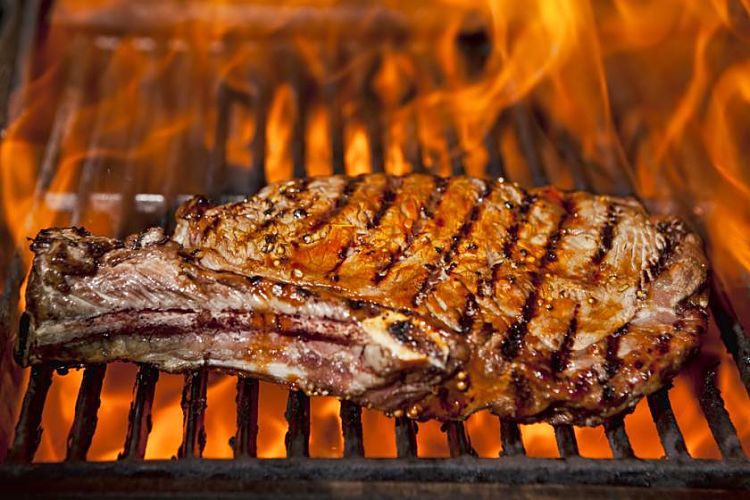
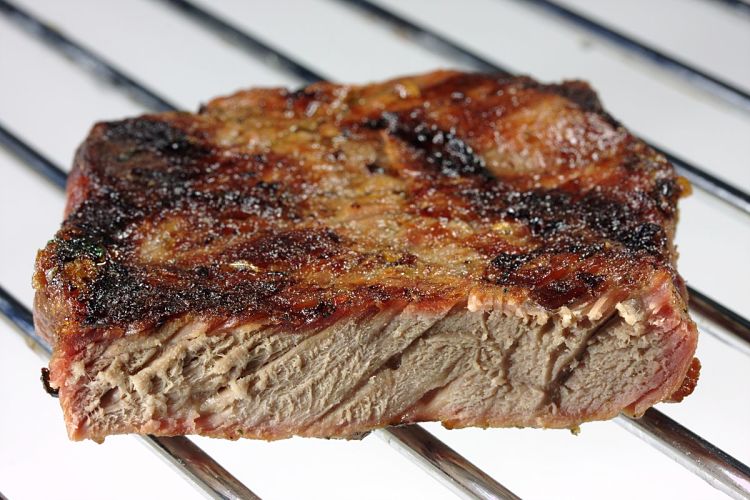
Glycation refers to the bonding of a protein or lipid molecule with a sugar molecule (such as glucose or fructose) producing glycotoxins, that are also referred to as Advanced Glycation Endproducts (AGEs). This process can occur within the body (via enzymes) or externally when food is cooked or prepared prior to being eaten. Cooking with temperatures over 250 degrees F (120 degrees C), such as frying and roasting, greatly accelerates the chemical reactions, especially when sugar is added to food being cooked, to brown or caramelize the food. Charred and over-cooked grilled and barbecued meats have high levels of glycotoxins.
However, these substances can also accumulate in foods at lower temperatures with long cooking times. Glyoctoxins are also added to many foods as flavor enhancers.
Many processed foods have high AGEs and glycotoxins, either due to processing or added ingredients. Some foods such as nuts have high natural levels of AGEs even when raw. Roasting of nuts increases the level of AGEs. Butter and margarine also has high levels. Food with moderate to high glycotoxins includes donuts, cookies, cakes, barbecued meats, processed meats and even some dark colored soft drinks. High levels of glyoctoxins are also found in fried or grilled meat, bacon, toasted bread, fried eggs and many foods that are browned or caramelized during the cooking. See the table below for a list of foods with the highest level of AGEs .
Link between Glycotoxins Dementia, Alzheimers and Diabetes
Recent studies showed that mice fed a diet rich in glycotoxins, at levels similar to typical Western human diets had:
- lower levels of sirtuins*, sometimes called the ‘longevity molecules’
- cognitive decline
- plaque deposits in their brains
- signs of insulin resistance, which is a precursor to diabetes.
Mice fed half the amount of glycotoxins did not experience these problems.
* Sirtuins have been shown to affect a wide range of cellular processes linked with aging, transcription, and inflammation. Suppression of NAD+-dependent sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) has been linked to dementia or Alzheimer’s disease and the metabolic syndrome. Sirtuins have also been linked with diabetes and aging processes.
A study of almost 100 healthy humans, over 60 years of age, supported the potential link between high glycotoxin levels and suppression of sirtuin levels in the blood, with cognitive impairment and insulin resistance.
Other animal studies have suggested that boosting sirtuin levels could increase life expectancy by up to 50 per cent.
Another study of 40 healthy subjects were randomly assigned to two groups. One group continued their typical Western diet that was rich in AGEs. The other group essentially ate the same foods but were encouraged to avoid grilling, baking or frying their food and to cook their food by poaching, stewing, or steaming their meals. The calorie and nutrient intake of the two groups was essentially the same.
After four months on the AGE-reduced diet, the level of various health indicators declined by as much as 60 percent.
Many researchers have suggested that dementia is Diabetes Type 3, because the development of insulin resistance may trigger dementia, because insulin is linked with brain health. A recent study using rats, showed that resistance to insulin interferes with fat metabolism in the brain.When the insulin metabolism in rats was induced artificially, it caused increased stress and inflammation in the brain and triggered symptoms similar to those of dementia.
A more recent research study suggests that increased AGEs levels in the diet, could trigger Alzheimer’s disease, insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome by causing chronic reduction in SIRT1 levels in the blood. Perhaps high levels of AGEs in foods is the common cause triggering reductions in SIRT1 and leading to both Alzheimer’s disease and diabetes, later in life.
While the research findings need to be confirmed, and do not prove a link between AGE and glycotoxins, and the increased risk of dementia and Alzeimers, changes in the way food is cooked and avoiding food high in added AGE may be warranted. Simple changes in diet and the way food is cooked may be beneficial.
How Can the Risk of Glycotoxins be Reduced?
You can reduce the number of glycotoxins in your food by cooking it at a lower heat.
This means avoiding the following cooking methods:
- Addition of sugar or sugar laden sauces during the final stages of cooking
- Caramelizing processes
- Frying of foods
- Charing of grilled and barbecued meats
- Crispy skinned food
- Microwaved foods (rather than just heating foods)
- Broiling foods
- Charring foods
Instead Use low temperature cooking methods such as:
- Steaming
- Stewing
- Boiling
- Poaching
- Using acidic ingredients such as lemon juice or vinegar
Avoid Natural Foods, Ingredients and Processed Foods Rich in AGEs
Many processed foods are rich in AGEs, either because of the way they are cooked or prepared or because AGEs are added as flavor or color enhancers. The table below provides a list of the foods with the highest level of AGEs.
The foods with highest glyoctoxins are:
- Bacon, smoked and Processed meats
- Grilled, fried and barbecued meats
- Nuts
- Cheese
- Mayonnaise and Sauces
- Butter
- Margarine
- Roasted peanuts and peanut butter
Advanced Glycation End Product (AGE) content of 100g of common foods, based on carboxymethyllysine test (see reference)
|
Food item
|
AGE kU (see reference) /100g serving
|
|---|---|
|
Bacon, fried 5 min no added oil
|
91577
|
|
Butter, whipped
|
26480
|
|
Chicken, skin, back or thigh, roasted then BBQ
|
18520
|
|
Margarine, tub
|
17520
|
|
Cheese, parmesan, grated (Kraft)
|
16900
|
|
Beef, frankfurter, broiled 450°F, 5 min
|
11270
|
|
Pine nuts (pignolias), raw (Bazzini’s Nut Club)
|
11210
|
|
Chicken, skin, thigh, roasted
|
11149
|
|
Chicken, skin, leg, roasted
|
10997
|
|
Cream cheese, Philadelphia soft, (Kraft)
|
10883
|
|
Beef, steak, pan fried w/olive oil
|
10058
|
|
Chicken, breast, breaded, oven fried, 25 min, with skin
|
9961
|
|
Cashews, roasted
|
9807
|
|
Chicken, breast, breaded, deep fried, 20 min
|
9722
|
|
Beef, steak, strips, stir fried with 1 T canola oil, 15 min
|
9522
|
|
Mayonnaise
|
9400
|
|
Chicken, selects (McDonald’s)
|
9257
|
|
Bacon, microwaved, 2 slices, 3 min
|
9023
|
|
Turkey, burger, pan fried with cooking spray
|
8938
|
|
Chicken, back or thigh, roasted then BBQ
|
8802
|
|
Whiting, breaded, oven fried, 25 min
|
8774
|
|
Cream cheese, Philadelphia original (Kraft)
|
8720
|
|
Cheese, American, white, processed
|
8677
|
|
Chicken, nuggets, fast food (McDonald’s)
|
8627
|
|
Cheese, feta, Greek, soft
|
8423
|
|
Peanuts, cocktail (Planters, Kraft)
|
8333
|
|
Chicken, dark meat, broiled, inside, 450°F, 15 min
|
8299
|
|
Turkey, burger, pan fried with 5 mL canola oil, 3.5 min, high heat
|
8251
|
|
Chicken, breast, with skin, 450°F, 45 min
|
8244
|
|
Turkey, burger, pan fried with cooking spray, 5 min, high heat
|
7968
|
|
Walnuts, roasted
|
7887
|
|
Chicken, crispy (McDonald’s)
|
7722
|
|
Peanut butter, smooth
|
7517
|
|
Beef, frankfurter, boiled in water, 212° F, 7 min
|
7484
|
|
Beef, steak, broiled
|
7479
|
|
Chicken, breast, breaded/pan fried
|
7430
|
|
Beef, steak, grilled 4 min, George Foreman grill
|
7416
|
|
Chicken, fried, in olive oil, 8 min
|
7390
|
|
Beef, steak, strips, stir fried without oil, 7 min
|
6973
|
|
Beef, steak, strips, 450°F, 15 min
|
6851
|
|
Cashews, raw
|
6730
|
|
Almonds, roasted
|
6650
|
|
Chicken, breast, roasted, 45 min with skin
|
6639
|
|
Peanuts, dry roasted, unsalted (Planters, Kraft)
|
6447
|
|
Turkey, ground, grilled, crust
|
6351
|
|
Chicken, curry, cube skinless breast, pan fry 10 min, broiled 12 min
|
6340
|
|
Margarine, tub, various brands
|
6220
|
|
Chicken, kebab, cubed skinless breast, pan fried, 15 min
|
6122
|
|
Beef, roast
|
6071
|
|
Chicken, roasted
|
6020
|
|
Turkey, breast, smoked, seared
|
6013
|
|
Turkey, ground, grilled, interior
|
5977
|
|
Tofu, sautéed, outside
|
5877
|
|
Chicken, breast, skinless, broiled, 450°F, 15 min
|
5828
|
|
Chicken, breast, skinless, breaded, reheated 1 min
|
5730
|
|
Chicken, curry, cube skinless breast, steam 10 min, broiled 12 min
|
5634
|
|
Cheese, brie
|
5597
|
|
Beef, ground, 20% fat, pan/cover
|
5527
|
|
Cheese, cheddar
|
5523
|
|
Sausage, beef and pork links, pan fried
|
5426
|
|
Beef, hamburger (McDonald’s )
|
5418
|
|
Chicken, breast, pan fried, 13 min high/microwave 12.5 secc
|
5417
|
|
Turkey, burger, broiled
|
5366
|
|
Chestnut, roasted, in toaster oven 350°F for 27 min
|
5353
|
|
Tuna, broiled, with vinegar dressing
|
5150
|
|
Chicken, thigh, roasted
|
5146
|
|
Tuna, broiled, with soy, 10 min
|
5113
|
|
Chicken, breast, pan fried, 13 min, high
|
4938
|
|
Beef, ground, 20% fat, pan browned
|
4928
|
|
Chicken, breast, grilled/George Foreman grill
|
4849
|
|
Sausage, Italian, BBQ
|
4839
|
|
Chicken, breast, skinless, roasted with BBQ sauce
|
4768
|
|
Pork, chop, pan fried, 7 min
|
4752
|
|
Cheese, Swiss, reduced fat
|
4743
|
|
Tofu, sautéed
|
4723
|
|
Sunflower seeds, roasted and salted
|
4693
|
|
Turkey, breast, roasted
|
4669
|
|
Chicken, leg, roasted
|
4650
|
|
Chicken, breast, skinless, breaded
|
4558
|
|
Cheese, Swiss, processed
|
4470
|
|
Pork, ribs, roasted, Chinese take out
|
4430
|
|
Shrimp frozen dinner, microwaved 4.5 min
|
4399
|
|
Turkey, breast, steak, skinless, marinated w/orange juice, broiled
|
4388
|
|
Salmon, broiled with olive oil
|
4334
|
|
Shrimp, fried, breaded (take out)
|
4328
|
|
Beef, meatball, potted (cooked in liquid), 1 hour
|
4300
|
|
Chicken, breast, strips, stir fried with canola oil, 7 min
|
4140
|
|
Tofu, broiled
|
4107
|