Energy Drinks: Side Effects, Health Concerns, Dangers with Alcohol
There is growing alarm about the negative health effects of highly caffeinated drinks, especially when mixed with alcohol. There drinks are very popular with teenagers and young adults, but there is little research on their long terms effects on young bodies.
These drinks have quite bizarre ingredients in high amounts and the effects of these ingredients alone, and in combination has not been tested. These drinks are also taken as a pick-me up after heavy drinking sessions and can be combined with other drinks in various combinations.
A recently review in the The Mayo Clinic Proceedings raised questions about both the safety and effectiveness of energy drinks, including their ingredients.
Health Risks of Energy Drinks
The early types of sports drinks, such as Gatorade were developed to re-hydrate and provide electrolyte and carbohydrate replacement, but they contained relatively small amounts of sugar. However these relatively simple types evolved into energy beverages that contained high sugar level, stimulants such as caffeine, and many weird additives. These energy drinks were being used outside of the sports and gym arenas, by “weekend warriors” and those seeking an advantage in endurance events.
Many teenagers and young adults take these drinks as a wake-up jolt to get started in the morning. However despite their widespread use and popularity, the long term side effects and the safety of these drinks has not been established. The Mayo Clinic Proceedings study reviewed the literature between 1976 and 2010 and summarized the findings on both the claimed benefits of energy drinks in enhancing performance and the potential negative side effects and health concerns.
No Long-Term Studies on Health Risks of Energy Drinks
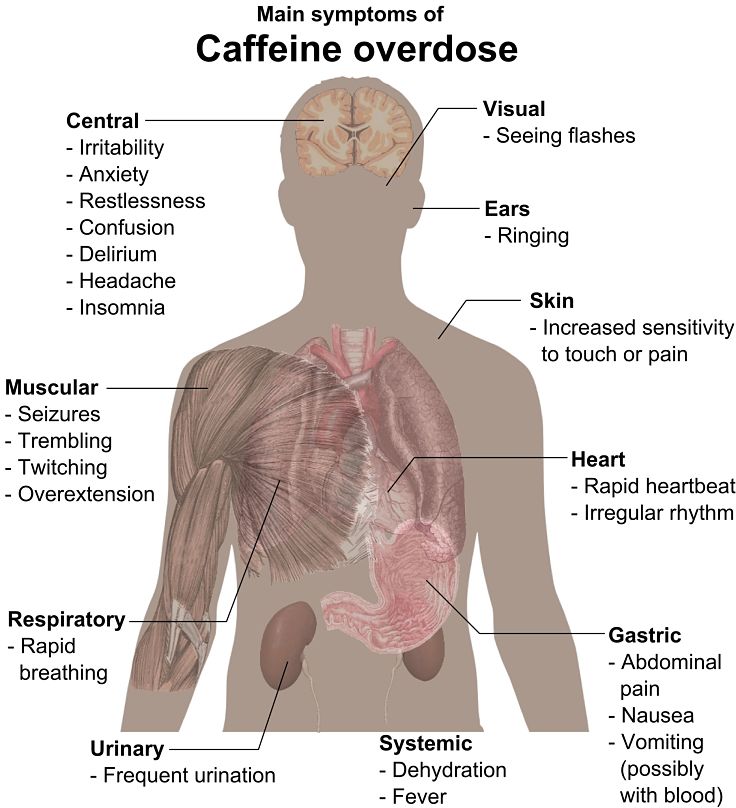
The researchers noted that the high levels of caffeine in the drinks posed a potential risk to certain susceptible people causing effects on heart rate, blood pressure and brain function. The authors noted that the literature contained 4 documented cases of caffeine-associated deaths and 5 separate cases of seizures associated with consumption of energy drinks.
There are numerous other less substantiated reports of side effects and negative responses. However most research studies done on energy drinks are very limited as they are based on very small sample sizes and the subjects are mostly healthy, young persons who would appear to be less vulnerable to displaying short-term ill effects. There no large scale, long term studies.
The potential long term effects such as insulin resistance, liver and cardiovascular disease, dental decay and diabetes are simply not known.
Many of the makers of these drinks have labelled them “dietary supplements,” which frees them from the regulations that apply to sodas and juices. It also allows them to add function claims about the products.
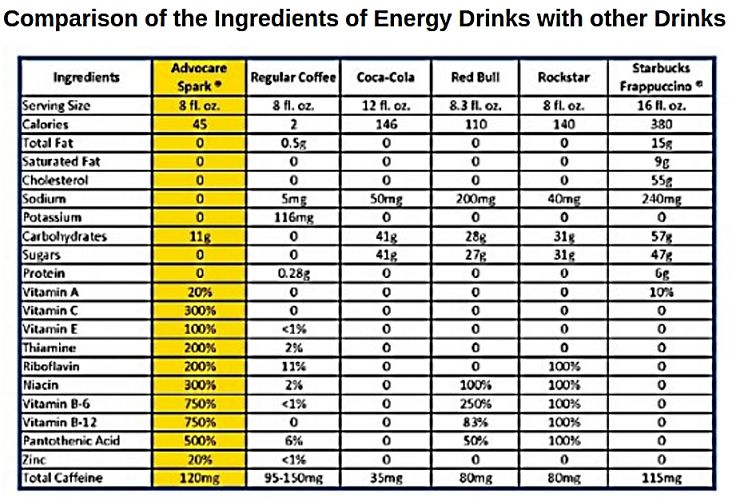
These drinks are equivalent to the caffeine in two or more cups of coffee, with loads of added sugar and other ingredients, that have not been adequately tested for their health effects. Anyone can buy these drinks, adults, teenagers and even 11- and 12-year-old kids who do not drink strong coffee.
Most of the mainstream makers of these drinks do add warnings for people sensitive to caffeine and a list ingredients. However the sensitivity to caffeine may be unknown as this may be the first way that young people with a vulnerability are exposed to high levels of caffeine.
Dangers when Energy Drinks consumed with Alcohol
Several states in the US have moved to ban 'Four Loko', an alcoholic beverage, that contained caffeine, guarana and taurine. The caffeine has subsequently been removed from this drink.
The concern is that the caffeine and caffeine-like ingredients in these drinks can hide the perception of inebriation and can increase the risk of drunken driving or other dangerous behaviours. Several college students have been hospitalized in recent months after consuming the drinks.
This danger also applies when energy drinks are consumed as the same time as alcohol, or after a heavy alcohol drinking sessions, and can lead to alcohol poisoning, car accidents and assaults in vulnerable people.
High Sugar Load in Energy Drinks
An athlete undertaking intense exercise who substitutes energy drinks for the common sports drinks, can have problems with the extra sugar load. So called 'Sports Drinks' such as Gatorade and Powerade, contain electrolytes and low amount of sugar. The high hit of sugar in energy drinks may interfere with the absorption of fluids and cause dehydration. The amounts of sugar in energy drinks is extremely high - A 16-ounce can of an energy drink may contain 13 teaspoons of sugar. The amount of caffeine is equivalent to the amount found in four or more colas. Caffeine, which is known to improve muscle action and performance, especially in endurance activities, is banned in many sports competitions.
Benefits of Energy Drinks
There is only limited research evidence that energy drinks can significantly improve mental and physical performance, driving ability when tired, and can decrease mental fatigue during long periods of concentration. In one study, 15 healthy persons aged 18 to 40 years
consumed 2 cans (500 mL) of a commercially available energy drink. The key effects were as follows:
- Within 4 hours of consumption, the maximum systolic blood pressure increased by 8% on day 1 and 10% on day 7.
- Within 2 hours of consumption, the maximum diastolic blood pressure increased by 7% on day 1 and 8% on day 7.
- Heart rate increased by 8% on day 1 and 11% on day 7.
- Throughout the study, heart rates increased between 5 and 7 beats/min, and systolic blood pressure increased by 10 mm Hg after consumption.
- No clinically important ECG changes were observed.
In a double-blind study of 68 healthy college-aged students showed that an energy drinks reduced the changes in blood pressure during a stressful experience and increased participants’ pain threshold. In another study a sugar-free energy did not influence high-intensity run time-to exhaustion. However, in a study of 6 male and 6 female trained cyclists improved cycling time-trial performance was noted after ingestion of a caffeinated
energy drink.
Other Ingredients in Energy Drinks
Many energy drinks include taurine, glucuronolactone, B vitamins, guarana, ginseng, ginkgo biloba and milk thistle.Taurine is an amino acid that occurs in high levels in animal products (such as lamb, beef, pork, chicken, etc.), and in most fish and shellfish. Taurine plays a role in neurological development and also assists in the regulation of water and mineral salt concentrations in the blood. It is added to energy drinks because some studies have reported that it may help to enhance athletic performance.
Guarana is a South American plant that is widely added to drinks and sodas in Brazil. Guarana contains very high levels of caffeine, and Guarana is added to energy drinks to further boost caffeine levels. Like caffeine it helps to boost the feelings of energy levels and improves mental and physical performance.
Ginseng is an herb that is claimed to provide a wide variety of potential benefits, including the creation of a sense of well-being and stamina. It is also claimed to help improve mental and physical performance and has many other health benefits.
B group vitamins can be found in a variety of natural foods and vitamins play an important role in regulating metabolism. These vitamins are often added to energy drinks because they contribute to the maintenance of mental function and metabolism, including conversion of the sugar added to the energy drink to boost energy levels.
Ginkgo biloba extract is produced from the leaves of the Ginkgo biloba tree. It has been used in traditional Chinese medicine for centuries. Ginkgo biloba extract has been reported to have antioxidant properties, help with vasomotor function, help with blood and circulation, and has a role in nerve transmission functions.
Carnitine, like Taurine, is derived from an amino acid and has a role in cellular energy metabolism. Some believe that carnitine can improve athletic performance (see Health Benefits of Creatine and How it Boosts Performance), but there little research to confirm this theory. Most people get sufficient amounts of carnitine in their diet and though the body’s natural production. Dietary l-carnitine supplements have been shown to increase the maximum oxygen a person can consume and to lower the respiratory quotient, and stimulate lipid metabolism.
Sugars are the basic energy source for the body, and many energy drinks have high levels of added sugar (as sucrose or high-fructose corn syrup). The consumption of glucose or other carbohydrates during, before and after prolonged exercise (>1 hour) has been shown to delay the onset of fatigue, conserve muscle glycogen, and improve performance.
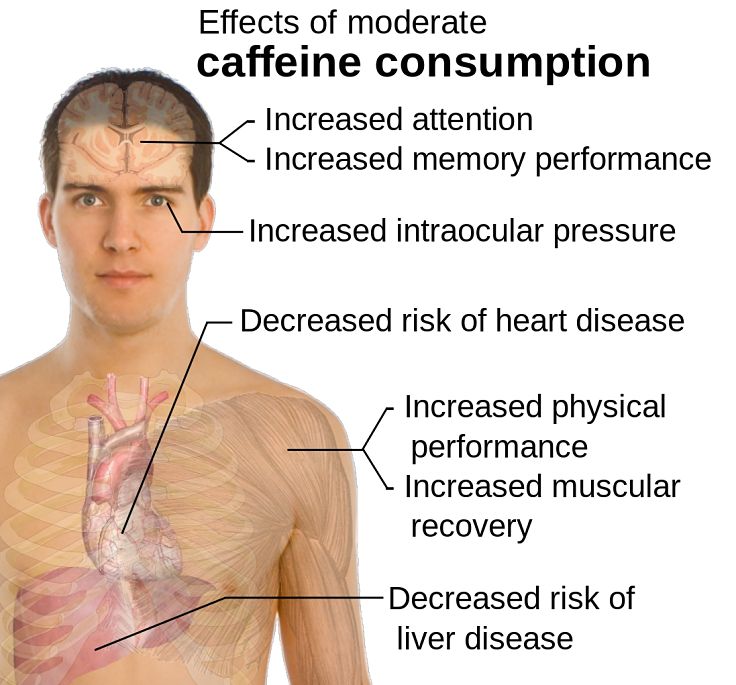
Caffeine - Most research shows ingesting caffeine an hour before exercise results in enhanced performance. It is a banned substance in high levels. Many endurance athletes believe that taking caffeine during long exercise sessions or races gives them an extra mental boost, increases concentration and focus, and provided increased motivation. The most dramatic performance improvements (from 20 to 50 percent) are seen during prolonged endurance exercise ( (over two-hours, such as a marathon).
The caffeine content of energy drinks varies widely. A 250 ml energy drink (about 8.5 ounces) can contain from 50-160 mg of caffeine. By comparison an average 8-ounce cup of coffee has about 100 mg caffeine, and a 12-ounce soft drink has about 40 mg caffeine. Moderate caffeine consumption for most individuals is about 300 mg per day and one energy drink can supply half that amount.
Does caffeine cause children to become hyperactive? There is no evidence that caffeine is associated with hyperactive behavior. Neither is caffeine is an addictive substance. When regular caffeine users suddenly stop drinking coffee or energy drinks, some people may experience mild symptoms such as fatigue, headache or drowsiness. These effects are usually mild and are not an addiction.
UPDATE:
Some young people gulp drinks such as Red Bull, Full Throttle and Rockstar to boost their energy, concentration and athletic performance.
But the caffeinated energy drinks don't appear to provide the purported benefits and can cause problems, including serious medical complications, says a review of the scientific literature published online today in Pediatrics.https://www.usatoday.com/yourlife/health/medical/pe...
The paper is already drawing criticism from the beverage industry, which says energy drinks have no more caffeine than a cup of coffee and aren't widely used by kids and teens
Conclusion
Energy drinks are generally safe for most people and can be drunk in moderation as part of a healthful diet. But it is important to check the number of servings in an energy drink bottle to determine the total caffeine content (read the label). You should also take account of the caffeine consumed from other sources, such as soda and coffee, when determining your total caffeine intake for the day. Use common sense, and talk to your kids about moderating energy drink consumption to agreed reasonable levels. It is not wise to substitute energy drinks for sports drinks during exercise. Avoid any combination of energy drinks and alcohol.